What are insulin pumps?
Written by:Therapy systems Continuous Infusion Insulin Subcutaneous (CSII) or insulin pumps is the use of electronic devices (microinfusoras) allowing continuous hormone administration through a catheter inserted subcutaneously.
It is certainly the best and most advanced way to treat type 1 diabetes, which is the type of diabetes most often affects children and adolescents, and is indicated for the vast majority of patients.
In addition, in consultations of Endocrinology at our disposal ISCI systems that integrate sensors allow interstitial glucose and adjust insulin doses more accurate and physiological form.
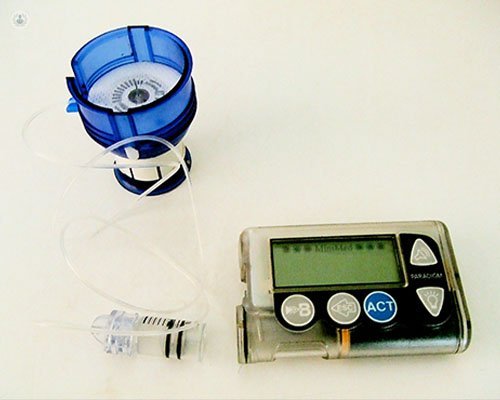
Benefits of insulin pumps
The benefits are many and in several areas:
- significantly increase the quality of life perceived by patients
- Decreases the incidence of complications (hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis)
- Allow to avoid using ultra-slow analogs insulin, which are replaced by a continuous ultra-rapid and more physiological manner similar to the function of the healthy pancreas of basal insulin infusion.
- Facilitate administration of multiple daily insulin boluses without receiving a puncture each time, making more flexible the dietary treatment.
- Models that are associated with continuous interstitial glucose sensors, predict and avoid hypoglycaemia by self-infusion suspensions. This is especially important in the case of young patients, of hypoglycemic unawareness or frequent nocturnal hypoglycemia.
Insulin pumps: how they work
The micro-infusor are programmed by the doctor and nurse educator based on the needs and characteristics of each patient and administer insulin through the catheter in small quantities and continuously. There catheters of different sizes depending on the age of the patient and are changed every 3 days, so it goes 5-6 punctures a day to one every 3 days.
The system instills a small amount of insulin continuously, comparable to watering trees "drip". Before each meal, with the help of the machine, the patient calculates how much insulin will need to cover the intake and gives the order to the pump to provide the dose you need and the best way to kind of food it will take.
Although there are already prototypes in experimentation and good result today patient interaction remains essential to the micro-pump to adjust the dose and timing of administration. Insulin pumps can not be considered at present artificial pancreas.
The knowledge and skills necessary for successful therapy system ISCI patients and their families are transmitted through a course during which we proceed to the implantation of the device. During the same they are reviewed and suited concepts already have on insulin therapy, diet (diet exchanges) and management of complications and special situations.
It is also taught to interpret the sensor readings interstitial glucose in combination with capillary blood glucose determinations. This course has subsequently continued as diabetes education classes and accompanying the diabetic patient periodically and continuously.
Risks of insulin pumps
Treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus using insulin pumps carries no special specific risk. Still, it is important to make a careful and responsible use of therapy, monitoring the operation of the device and attending scheduled alarms. Thus, you can deal with any incidents or circumstances in which insulin infusion is interrupted, such as in case of the presence of air bubbles in the system or kinking of the catheter.



