5 Key questions on diabetic retinopathy
Written by:Diabetic retinopathy is one of the long - term complications that can present diabetes. The retina is the most important structure for viewing eye because it is in charge of capturing the image we see for through the optic nerve to the brain and interpreted move it. Therefore, a deterioration in the retina, in this case diabetes result in an impaired vision may become significant and permanent.
According to the International Diabetes Federation, there are currently 415 million people diagnosed and it is estimated that by 2040, this figure will rise to 640 million; this is exacerbated because 1 in 2 adults with diabetes are undiagnosed, which is a social, health and economic problem of the first magnitude.
That is why it is important to note that control of diabetes and its complications begins in primary health care, which should include the detection of diabetic retinopathy, and early detection and timely treatment of diabetic retinopathy they can prevent vision loss.
What are the causes of diabetic retinopathy?
It is caused by the damage done to the blood vessels of the body and therefore also that nourish the retina, and this occurs as a result of high blood glucose levels maintained long.
Diabetes produces two types of vascular lesions in the retina:
- Increased permeability of small blood vessels, which determines the liquid outlet thereof causing a retinal edema when affects the macula (central retina), is called macular edema and produces a visual disturbance Central in the patient.
- Hemorrhages that can stay confined to the retina or extend the gelatinous contents of the eye (vitreous humor).
What are the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, lack of symptoms can make you go unnoticed. Symptoms that may occur include:
- Decreased night vision
- Changes in color vision (mostly blue and yellow)
- Poor recovery of vision after exposure to bright light
- Vision variation
- Blurry vision
- Episodes of diplopia
In advanced stages and the most important symptom is loss of vision that the patient notices; This loss of vision can be seen in the center of the image caused by diabetic macular edema or even a total loss to a massive hemorrhage in the vitreous occur.
Notably, to display symptoms, pathology must be in advanced phases, but in this situation the treatment is not as effective. It is therefore better control of retinopathy before symptoms appear.
What types of diabetic retinopathy exist?
Diabetic retinopathy has different phases:
1. No apparent retinopathy their appearance is normal, since no lesions are seen in the fundus.

2. Mild nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: you can see some small rounded red dots called microaneurysms.

3. moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: has small retinal hemorrhages and exudates or white stains.
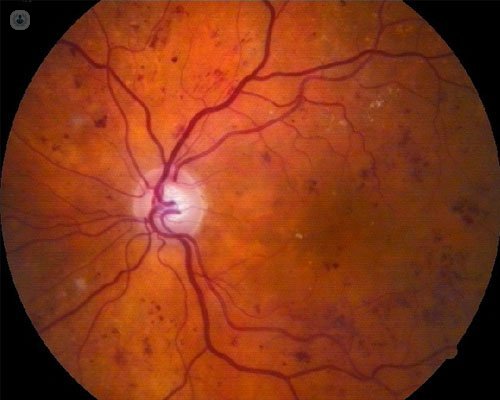
4. severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: occlusive vascular lesions and intraretinal hemorrhages throughout the retina are formed, which stimulates the emergence of new fragile retinal vessels and spread throughout the retina.

5. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy: retinal new vessels break and cause bleeding into the vitreous humor, which stimulate the formation of scar flanges, with traction of the retina and the consequent emergence of retinal detachments.
How you can diagnose diabetic retinopathy?
It is very important that anyone who has been diagnosed with diabetes go to the eye doctor to get checked out at that time and repeat it annually or biannually depending on the evolution of diabetes.
Ophthalmological examination should include the following tests:
Eye examination: central vision is measured, visual acuity, eye strain and the anterior surface of the eye.
Fundus examination: is to dilate the pupil to better analyze the most peripheral areas of the retina. The scan can be performed with different instruments such as the ophthalmoscope hand (direct ophthalmoscopy) or binocular ophthalmoscope (indirect ophthalmoscope) and with lenses exploration that are placed over the eye and help the use of the lamp or retinograph for eye image archive.

Fluorescein angiography: to view the deep vascular network of the eye. It is performed when there are hurt on the back of the eye.

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a technique that captures a very accurate picture of the different layers of the retina. It is very useful in cases of macular edema.

What is the treatment of diabetic retinopathy? 
As it mentioned above, must be borne in mind that early diagnosis and treatment can prevent vision loss, ie, a person with diabetes can live their whole lives without eye always problems when under proper ophthalmologic control and knows how to live with this disease (medication, healthy diet and adequate physical activity).
So in the early stages of the disease, the only treatment is to control diabetes. When you have already detected significant vascular disorders, treatment is laser photocoagulation, which helps stabilize retinopathy reducing abnormal and fragile blood vessels and preventing rebleeding, but not cure it.
When macular edema appear, they can not be treated with laser, so it requires a very specific medication (anti-VEGF or dexamethasone) that is given by injection into the eye.
Finally, if there is an alteration in the vitreous humor, either flanges that can move the retina or by repeated bleedings, treatment is surgery, specifically by a technique called vitrectomy, which involves the removal of vitreous opacified blood.


