The endoablative techniques of the present
Written by:Safenectomy or stripping has been the technique of choice for the treatment of varicose veins for nearly a century. Classic varicose vein surgery had two objectives: to eliminate and correct venous hypertension, based on two basic concepts: excision and radicality. However, in the mid-1990s, other goals emerged, such as minimizing complications, reducing the socio-labor gap, and obtaining the best possible cosmetic outcome.
Today there are different techniques and modalities.
Endoblastic techniques: the endolaser
Laser technology is used in medicine in numerous fields. Under the concept of selective photothermolysis, the laser emits a light wavelength of light directed at the chromophore of the target tissue. The first generation of lasers used a wavelength of between 800 and 1000 nm, directed mostly to the hemoglobin chromophore, while the new ones have a wavelength of between 1300 and 1600 nm, and are mainly addressed to the water chromophores and cells of the endothelial wall, causing injury to the vein wall.
Since the beginning of its use, laser technology has been involved in numerous controversies. In fact, the choice of wavelength is still a matter of debate. There is a clear tendency for a laser with higher wavelengths, as well as the use of fibers with radio waves, to have better results on the quality of life of the patient.
Endoblative techniques: radiofrequency
There is knowledge of the use of radiofrequency for the treatment of superficial venous insufficiency since 1998 in Switzerland. The first effect of the radiofrequency is the concentration of the collagen and later the denaturation of its matrix. Other factors, such as venous spasm, endothelial denudation and wall edema, are involved in the evolution towards the fibrotic closure of the vessel.
There are many works that have compared the radiofrequency with other techniques, initially with conventional surgery, and later with the endolaser. The radiofrequency and the endolaser of 1470 are the most effective and less harmful modalities, offering very similar results.
Endoblative techniques: water vapor
The system of pulsating water vapor at 120 degrees centigrade to cause occlusion of insufficient saphenous axes has been the last thermal ablation technique to be incorporated. Although he had been talking about the procedure for some years, it was characterized from the beginning by a scarce bibliographical. .
However, subsequent scientific evidence has shown occlusion rates at one year similar to other means.
Water vapor is a thermal ablation system that requires, or is advisable, the use of tumescent anesthesia, a technique of local anesthesia consisting of the infusion of an important volume of a solution at low concentration of local anesthetic and adrenaline.
Although there are numerous enthusiastic publications regarding its efficacy, it has not reached the diffusion of other endovascular techniques. The system, devised in France, appeared in its first moment as an alternative to the endolaser and the radiofrequency, for the cases of tortuous and superficial saphenous axes. The catheter is clearly thinner than the radiofrequency catheter, and allows you to navigate non-rectilinear veins.
Endovascular techniques: eco-guided sclerotherapy
As early as 1939, McAusland injected foam air into varicose veins with a therapeutic goal. However, sclerotherapy casts an endless number of doubts: what sclerosant to use? At what concentration? How to make the foam? How to inject the foam, if with catheter in withdrawal or direct puncture? There are many questions with no definitive answer.
In general, truncal sclerotherapy offers less local morbidity than thermal ablation in nerve lesions, although it leads to higher rates of thrombophlebitis and pigmentation. Although their results can be considered acceptable, it is the modality with the highest failure rates.
Endoblative techniques: mechanical-chemical ablation
Through a minimally invasive catheter with double action on the one hand, mechanical, with a guide that rotates at 3500 rpm causing a spasm of the venous endothelium, and another chemistry, by infusion of the sclerosing agent that induces the fibrosis of the vein, eliminating the need for tumescent anesthesia.
Mechanical-chemical ablation has proven to be a safe and effective process in its initial studies.
But not all is reduced to occlusion rates, the Van Eekren study compares radiofrequency and mechanical-chemical ablation for patients with varices, obtaining favorable results the MOCA system in relation to the perioperative pain, improvement of the quality of life and recovery of the daily activity. In a multicenter study, Bootun also found advantages in the MOCA system over radiofrequency.
Endo-adhesive techniques: adhesive sealing
The adhesive Cyanoacrylate (Venaseal) has a long life in medical applications, especially in cerebral arteriovenous malformations. The adhesive properties of cyanoacrylate and its first medical applications go back to 1951. Derivatives used in medicine are n-butyl esters, which provide strong and rigid bonds. Its application in chronic venous insufficiency has been achieved after planning some modifications, such as giving the glue greater flexibility to tolerate dynamic movement of the legs, a rapid polymerization in contact with blood and tissues, and especially a higher viscosity for the purpose to eliminate the risk of embolization to deep venous system and pulmonary circulation.
The procedure does not require tumescent anesthesia or postoperative elastic compression. Given the need not to use elastic compression stockings, one of the points where there is no consensus on ideal postoperative compression therapy is obviated.
Analysis of procedures in endoablative techniques
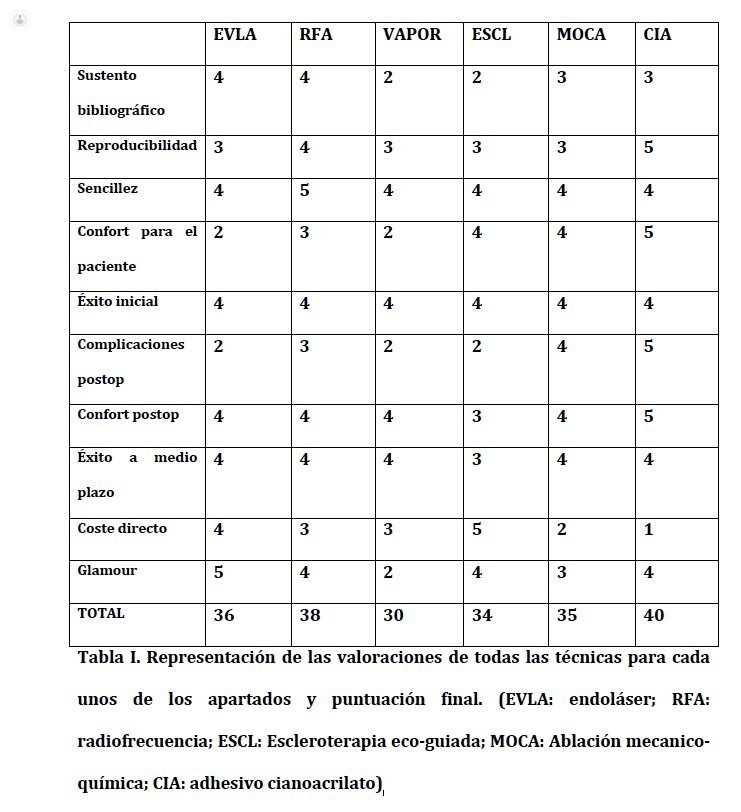
To try to make a global and personal assessment of each of the techniques, some parameters have been selected that could be grouped into different categories. However, a complete cost analysis has not been done, since it is difficult to include all the concepts, such as the personnel needed for the procedure, the time spent for each one, the location in an operating room or ward or the repercussion economics of low socio-labor are difficult to quantify and compare.
The categories are:
- Bibliographic support and scientific evidence: the oldest techniques (EVLA and Radiofrequency) will have greater scientific support.
- Reproducibility: this section evaluates if the procedure is applicable to as many patients as possible. Thus, we must take into account situations such as trying to avoid MOCA and sclerotherapy in large veins, thermal ablation in very thin patients, extrafascial veins ...
- Simplicity: aspects such as the learning curve or the average time consumed per procedure. In this case, radiofrequency would be the best. The Venaseal device consumes a little more average time. Sclerotherapy and endolaser have a certain variability factor, and the MOCA system requires a higher learning curve.
- Comfort for the patient: important aspects as a place of treatment, whether or not tumescent anesthesia or sedation is necessary, the pain generated by the procedure ...
- Initial success: only occlusion rates are taken into account, where all procedures are very similar.
- Postoperative complications: pain, tombo-phlebitis, nerve damage ... The radiofrequency seems to have demonstrated superiority with respect to the laser, although the latest novelties seem to overcome the radiofrequency.
- Post-operative comfort: need for elastic containment, prohibition of sun exposure, risk of pigmentation ... The Venaseal device offers advantages in this section.
- Medium-term success: occlusion rate, recanalizations, need for re-treatment ... Eco-guided sclerotherapy offers the worst results in this section.
- Direct cost: despite being an unrealistic section, since we only focus on the price of the devices and necessary material, the Venaseal device is expensive compared to the rest, with sclerotherapy and endolaser being the most economical in terms of direct cost material.
- Glamor: it values the fascination, the seduction ... In short, its capacity of diffusion. In this case, the laser is imposed, although radiofrequency and foam have gained ground in recent years.
Endoablative techniques, constant advances and a promising future
If, by itself, endovascular techniques in the treatment of superficial venous insufficiency due to incompetence of saphenous axes were a great advance in comparison to conventional surgery or other open techniques, in concepts such as less aggressiveness and faster socio-labor recovery, they evolve even more to eliminate cosmetic complications and side effects such as paresthesia and ecchymosis, in addition to avoiding the classic operating room as a place for the realization.
No paresthesias, absence of pigmentation, no surgery, no medias ... They are attractive aspects for patients.



