Coronary heart disease:causes, symptoms and treatments
Written by:Coronary artery disease, also known as coronary artery disease is a condition in which plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, which is the muscle of the heart.
Causes of heart disease
The most frequent cause of coronary heart disease is the atherosclerosis, when plates are produced inside the coronary arteries. These plates are formed by cholesterol, various fatty compounds, calcium, and fibrin, which is procoagulant. There are two types of plates:hard and soft plaque plate 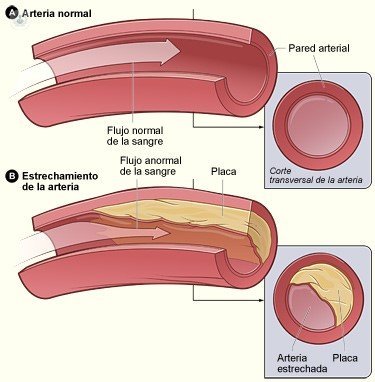
-The hard plate usually grows gradually and there comes a moment causing an imbalance and/or interruption between the blood supply to the heart muscle and it needs causing what is called angina pectoris and/or myocardial infarction.
-Soft plaque usually evolves differently and mediation is conditioned by the existence of an inflammatory process that triggers the coagulation process and may completely obstruct the lumen of the coronary artery causing sudden way or acute myocardial infarction.
Some of the factors that increase the chance of heart disease are:
• high cholesterol
• hypertension
• diabetes
• a diet high in saturated fat
• Overweight
• sedentary
• too much stress
• Smoking
• have close relatives with heart disease at an early age
Symptoms of heart disease
You may not know you have heart disease until they begin to have symptoms of blockage in the arteries. The chest pain ( angina) and shortness of breath are often the first signs of coronary artery disease. Some people do not know they have heart disease until they have a heart attack.
If you have multiple risk factors should talk to your doctor even if you have symptoms. There are some steps you can take to reduce risks and improve the health of the heart and blood vessels.
A person may suffer from coronary disease for many years without showing symptoms. This slow the disease process can start in childhood. In some people, the disease can cause symptoms between 30 and 40 years of age, while others have no symptoms until after 50 or 60 years. But with increasing the degree of obstruction, but reduced flow of blood to the heart can start to cause what is called angina.
Some patients with coronary artery disease can not suffer symptoms of angina. Sometimes poor oxygen supply to the heart (which is called ischemia ) does not cause any pain. This is called silent ischemia.
Another way of presenting coronary disease is the MI, which is caused by a complete blockage of the coronary artery. The obstruction of the coronary artery prevents oxygen-rich blood reaches and nutrients to a section of heart. If blood can not reach the heart muscle, this morira. If you get treatment immediately, you can reduce the damage, but a section of heart muscle dies, the damage is irreversible.
Treatments for heart disease
1. Drug:Several medications help relieve the pain of angina caused by coronary artery disease. People with severe angina often receive several different medications. They can also be administered as aspirin antiplatelet patients suffering from angina, since these medicines reduce the chances of blood clots forming in places that are unobstructed.
• A medicine called nitroglycerin can widen or dilate the arteries and thus improve blood flow to the heart.
• Beta blockers« block»the chemical messages that the heart receives and that could make you work more than necessary.
• Calcium channel blockers help keep arteries and reduce blood pressure by relaxing the smooth muscle that surrounds the body's arteries open.
2. Percutaneous Interventions:The angioplasty opens the narrowed arteries, is a procedure performed by interventional cardiologists using a laquo long, thin tube called &;catheter»carrying a small globe (or ball) at the tip, which inflated at the site of the obstruction of the artery to compress the plaque against the artery wall. Angioplasty is also called percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty ( PTCA).
The angioplasty balloon is complemented by the placement of a stent. The stent is a tubular metal mesh that is implanted in the area of the artery blocked by plaque. Current stents are coated with drugs that reduce the possibility that the artery from closing again. These are called drug-eluting stents 
The rotational atherectomy can be another option for those patients with balloon angioplasty is ineffective because of the hardness of the plate so this device has on the distal portion of the catheter deep olive small diamond crystals surrounded by rotating at high speed ( between 160,000 and 190,000 ) per minute and cutting hard plate and then continue with stenting.