Addressing psoriasis in children early and effective
Written by:Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder in which they appear red plaques covered with thick scales, which are repeated in outbreaks throughout life. This is a relatively common condition, affecting 1 to 2% of the population and can occur at any age, from infancy to adulthood. However, one third of patients develop the condition before age 20.
Although there is no cure for psoriasis, specialists in Child Dermatology do have many treatment options now also for children, which vary depending on the intensity and location of the lesions.
 Causes of psoriasis
Causes of psoriasis
It is not yet known what causes psoriasis, but it is known that genetics and immunology play an important role in its development. In patients with psoriasis, the immune system is activated an abnormally, resulting in an acceleration of the growth cycle of skin cells. Rather than discard, the most superficial cells accumulate, forming thick scales on reddened skin areas.
There is a clear family factor. If one parent suffers from psoriasis, there is a 25% chance that each child's suffering. Some factors can trigger or intensify psoriasis in children, such as skin damage and infections. Up to half of children with psoriasis have a resurgence of the disease from 2 to 6 weeks after diseases such as respiratory or digestive infections. Nevertheless, psoriasis is not a contagious disease.
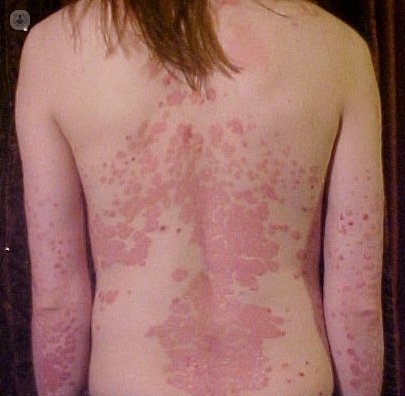
Symptoms of psoriasis in children
Psoriasis occurs regularly as plates skin dry, red and scaly which can be very itchy. Sometimes it can also cause burning and come and go unpredictably.
There are many forms of presentation of the disease, but the most common in children is plaque psoriasis. It may be limited to a few plaques or affect large areas of skin. It can appear in any area but most commonly affects the back of the elbows and knees, and scalp. Guttate psoriasis, where the rash takes the form of small lesions gotas- is another frequently in children. The face and the genital region are often affected in young children. Psoriasis can also affect the nails (especially as small depressions or dimples in the nail plate), and joints (psoriatic arthritis).
How to diagnose psoriasis
To diagnose psoriasis there are no specific blood analytical. The diagnosis is clinical and is made from the skin lesions. If in doubt, you can perform a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes.
Emotional considerations in children with psoriasis
For many children the main problem of psoriasis is its visibility and the effect this may have on their self - esteem. Children with psoriasis have an increased risk of depression and anxiety. Psoriasis does not leave scars on the skin but can cause emotional scars.
Treatment of psoriasis in children
The treatment of childhood psoriasis depends on the severity, extent and type of psoriasis. Most of them reduce skin inflammation, while others reduce flaking and itching. Treatments vary from creams, shampoos and ointments to ultraviolet light phototherapy and systemic medication in the most important cases. There is no medication that works in all patients and may take some time to get the appropriate treatment regimen for each child.
In this sense there:
- Topical treatment. Topical medications are applied directly on the psoriasis plaques. Contain cortisone derivatives or other anti-inflammatory corticoids products such as vitamin D3, tar, salicylic acid and retinoids. They can be applied in isolation, but often occur in products that combine. moisturizers are also used to maintain good skin hydration and reduce itching, dryness and scales.
- Phototherapy with ultraviolet light. When topical drugs are not effective, or the damage is very extensive, some children may be treated with ultraviolet light. Phototherapy uses ultraviolet light to reduce skin inflammation. Natural light contains ultraviolet light and can be recommended by child dermatologist. Although natural light can be helpful, too much exposure and sunburn can lead to an outbreak of psoriasis at the affected site and increase the risk of premature aging and skin cancer. Phototherapy is done 2-3 times a week at the doctor's hospital.
- Oral and biologics. The most severe forms of psoriasis require oral medication, or by infusion or injection into the body ( "biological" drugs). These treatments have risks and benefits should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
Important considerations in childhood psoriasis
Children with psoriasis have an increased risk of developing obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease in adulthood. That is why we must make a healthy diet, maintain ideal weight, and exercise regularly.


