Osteoarthritis of the knee: Symptoms and Treatment
Written by:
What is osteoarthritis of the knee?
Cartilage is a smooth connective tissue that acts as a buffer and protective pad between the contact surfaces of the bony structures that constitute the knee. That is, the femur, tibia and patella.
Osteoarthritis develops when cartilage deteriorates and bone surfaces rub each other without their protective pad, causing wear. The articular bone surfaces harden, growing in its peripheral region, and bony outgrowths form osteophytes.
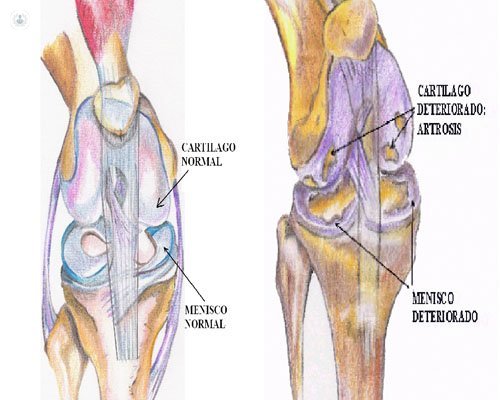
Symptoms of osteoarthritis in the knee
The main symptom of osteoarthritis of the knee is that daily activities become painful and difficult, reducing the quality of life.
The knee has within the synovium, which produces a fluid that feeds the cartilage and keeps sliding. When there osteoarthritis occurs in as much fluid than normal, this is what is known as "fluid in the knee". You can specify puncture to remove it.
The patient will also present difficulty bending or stretching the knee, as well as blockages, failures or feeling of instability.
When osteoarthritis is advanced causes deformity in the knee and impaired limb alignment.
Pain and swelling are worse in the morning, after a period of inactivity, after walking up and down stairs. Increases with climate change.
Prevention of knee osteoarthritis
There are several factors that can increase the chance of developing osteoarthritis in the knee:
- Excess weight.
- hereditary factors.
- Age. The cartilage has deteriorated more difficult to recover over the years
- Females.
- The presence of previous injuries not intervened: menisci, cruciate ligaments and cartilage.
- Professions or activities that must be kneeling or squatting. As well as lifting overweight or practice of high impact sports.
- Developing rheumatoid arthritis, gout or change in alignment of the lower limb.
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis
There are two main treatments of knee osteoarthritis, non-surgical or conservative treatment and surgical treatment.
- Treatment Non - Surgical or Conservative:
- Changing the rhythm of life. Lose weight, avoid activities like climbing stairs, change the type of sports activity, avoiding any harmful activity for the knee.
- Help of canes, crutches, knee. Also, application of local cold by ice or gel.
- Use of oral medications or by intra-articular infiltrations.
- Surgical Treatment. It denotes him as osteoarthritis does not respond to conservative treatment or nonsurgical. Specialists in Traumatology use various techniques:
- Arthroscopic surgery. It consists of a cleaning intra-articular. Only it provides relief of symptoms in the short term.
- osteotomy. To correct limb alignment is achieved
download the compartment of the knee most affected by osteoarthritis.
- unicompartmental prosthesis. When only damaged part of the knee, internal or external, a prosthesis is implanted small. It requires only a small incision in the knee.
- Arthroplasty or total knee replacement. It is the final recommendation for a patient with disabling pain and other rebel knee


