Neurophysiology utility in the diagnosis of eye diseases
Written by:Neurophysiological various tests to detect and differentiate eye diseases: retinopathy, maculopathy, optic neuropathies.
Neurophysiology based diagnostic obtaining physiological signals, upon application, in general, specific stimuli, whether electrical, audio or visual, as in the field in question. Their analysis provides important information not be feasible obtained by macroscopic visualization. In general, a signal is obtained whose waveform amplitude or latency can provide us with information about the stimulus conduction velocity until receiving organ or axonal respectively density.As experts say in Clinical Neurophysiology it is important to know that this kind of signals we provide data of great relevance, sometimes impossible to meet otherwise, and can anticipate the ophthalmologic diagnosis before it's visible in the fundus .
Ophthalmic anatomic considerations
First of all, and for a better understanding, we will briefly review the characteristics of the retina, as well as the cells involved, whether in the perception of the stimulus and transmission.Light enters the eye through the cornea, crosses the anterior chamber, lens and vitreous humor and reaches the retina. Once here through all layers to finally interact with the photosensitive cells: rods and cones.
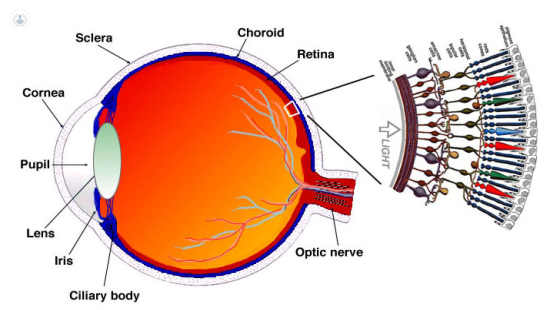 In the center of the retina is a circular area, the papilla, which corresponds to the optic nerve. The macula is an ill-defined area in the posterior pole of the papilla superior size and located next to this. The central part of the macula is the fovea and the center, foveola.
In the center of the retina is a circular area, the papilla, which corresponds to the optic nerve. The macula is an ill-defined area in the posterior pole of the papilla superior size and located next to this. The central part of the macula is the fovea and the center, foveola.
 The retina, in turn, consists of several layers whose innermost layer would be the pigment epithelium which connects directly to the rods and cones.
The retina, in turn, consists of several layers whose innermost layer would be the pigment epithelium which connects directly to the rods and cones.
 The pigment epithelial cells are supporting cells modified by the presence of a pigment that absorbs light without participating in the vision, while limiting propagation of photons. The photoreceptors (rods and cones) also have another pigment, opsin, who do participate in the chemical mechanism of vision.
The pigment epithelial cells are supporting cells modified by the presence of a pigment that absorbs light without participating in the vision, while limiting propagation of photons. The photoreceptors (rods and cones) also have another pigment, opsin, who do participate in the chemical mechanism of vision.
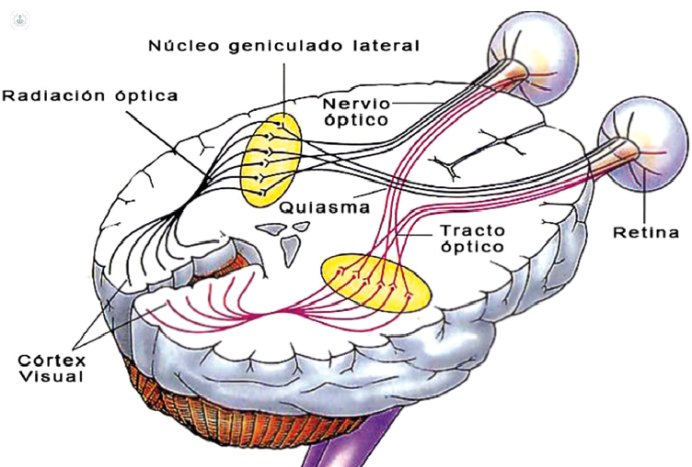
In the outer plexiform layer, axons (extension of specialized neurons in conducting nerve impulses) of the rods and cones synapse or connection with the dendrites (branches of the neuron) -the 1st neuron cell and with a bipolar horizontal cells. The bipolar cell connected in the outer plexiform layer with the 2nd neuron - ganglion cell - and also with amacrine cells. The axons of the ganglion cells form the nerve fiber layer, through the optic nerve, reach the outer geniculate body where they synapse with neuron axons 3rd through optical radiation, reaching the cortical cortex.
 Moreover, it notes that the distribution of rods and cones is not uniform across the retina. So, we differentiate the macular retina, densely cones and peripheral retina where rods predominate. This is important to differentiate the utility of the different techniques in the study of diseases that most affect the peripheral retina against which most affect the macula or macular diseases.
Moreover, it notes that the distribution of rods and cones is not uniform across the retina. So, we differentiate the macular retina, densely cones and peripheral retina where rods predominate. This is important to differentiate the utility of the different techniques in the study of diseases that most affect the peripheral retina against which most affect the macula or macular diseases.
Neurophysiology techniques for detecting eye diseases
Electroretinography (ERG) full field or ganzfeld (GERG). Assesses the overall responses of the retina rods and cones differentiating. It is useful for diagnosis of retinopathy.Electroretinography (ERG) with checkerboard pattern (PERG). It uses a structured stimulus pattern with black and white squares that reverse with a certain frequency and selectively stimulate ganglion cells are concentrated mainly in the macular area. We used to study the maculopathy.ENP pattern. Like the above, selectively stimulating the ganglion cells, although registration is done at the level of cortex. It has traditionally been used to study the optical neuropathies, especially demyelinating diseases, although its diagnosis is limited if there is a maculopathy. It is therefore advisable to conduct simultaneous pattern ERG and time valuing central driving between cornea and visual cortex to differentiate an optical neuropathy maculopathy.ENP flash. Unlike the previous one, it does not require collaboration, which is usually performed in children and noncompliant patients or simulators. However, its diagnostic value is very limited and only allows us to affirm the continuity of the light stimulus to the visual cortex.Electroretinography (ERG) multifocal. 30º core values topographically central retina where the macula is. Its primary use is in the diagnosis of macular diseases.Electro-oculogram (EOG). Assesses the integrity of the pigment epithelium.


