Thrombosis: what it is and how to prevent it
Written by:Thrombosis is the formation of a clot within a blood vessel, vein or artery, caused by different causes, such as altering blood vessels (atherosclerosis or trauma) or altering coagulation factors (thrombophilia).
Causes of thrombosis
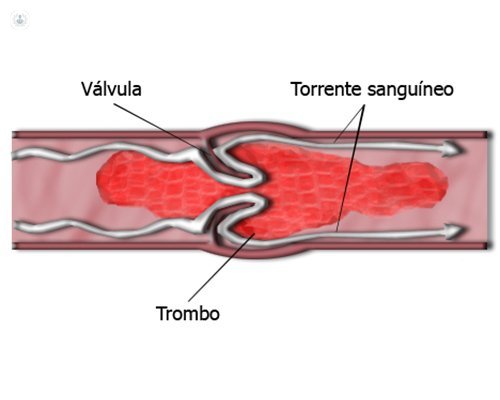 There are different factors that can favor the formation of thrombosis, such as staying in bed for a prolonged period or surgery. There are also other preventable factors favoring thrombosis such as smoking, poor diet and obesity.
There are different factors that can favor the formation of thrombosis, such as staying in bed for a prolonged period or surgery. There are also other preventable factors favoring thrombosis such as smoking, poor diet and obesity.
Symptoms of thrombosis
Symptoms that occur thrombosis are varied depending on the affected area and whether it is a venous or arterial thrombosis.
Venous thrombosis, which affects the lower limbs, manifested as pain, redness and swelling of the leg abruptly.
However, another type of venous thrombosis is affecting varicose veins and superficial manifested as pain, redness and local hardening of varicose path. Superficial vein thrombosis is directly related to varicose veins and has a minor medical significance.
The lower limb arterial thrombosis occurring acutely causes lack of limb perfusion abruptly. Clinical manifestations coldly, paleness, functional impotence and severe foot and leg pain.
Consequences of thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis in lower limbs, belatedly, can produce postflebítico syndrome, which manifests as edema, pain and skin involvement, even to develop chronic ulcers.
Most acute complication of DVT is the mobilization of a thrombus that was originally in the legs to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism is a medical emergency that manifests clinically with pain in the chest, shortness of breath, coughing, sometimes with blood (hemoptysis) and in severe cases, hypotension and even loss of consciousness.
Arterial thrombosis in the lower limbs, if left untreated, can cause damage to the tissues and structures that are not irrigated and may reach myocardial tissue and gangrene.
Treatment of thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis of the lower limbs treated with anticoagulant medications and therapeutic elastic support stockings with. Early diagnosis and initiation of treatment as soon as possible to reduce acute complications, sometimes severe, and possible chronic effects, such as edema and ulcerations in the legs.
Thrombosis varicose paths is heparin at lower doses of corticosteroids and topical creams. In a second assessment it would require a vascular surgeon to raise the surgery of varicose veins.
Arterial thrombosis of the lower limbs requires an urgent assessment by a vascular surgeon to indicate the best treatment, sometimes with blood-thinning medications or fibrinolytic, breaking clots, and sometimes by surgical treatment such as bypass, stents, etc. .
Prevention of thrombosis
Currently, there is a great awareness by both the health sector and by patients, prevention of thrombotic events.
Venous thrombosis can be prevented with early ambulation after interventions, shortening of hospital admissions and the use of prophylactic heparin when deemed necessary.
Arterial thrombosis can be reduced with a reduction in cardiovascular risk factors, ie, by controlling blood pressure and diabetes, good nutrition and smoking abstention.


