Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Written by:Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects nearly 5% of women. This is an ovulatory dysfunction caused by a hormonal imbalance that can affect women in different ways, interfering with their reproductive function.
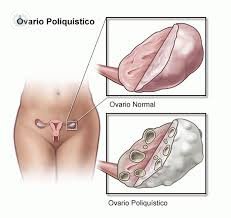
Many hormones that are affected by this pathology: estrogens, progestins, androgens, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), etc.. These hormonal changes have the consequence that small cysts in the ovaries (which can be easily visualized by transvaginal ultrasound) and increased levels androgens (male hormones) in the blood occurs, which results in some clinical manifestations appear.
These alterations involve the main manifestation of polycystic ovary syndrome, which is anovulation, ie, the absence of ovulatory cycles. For this reason, patients have amenorrhea (absence of rules) or opsomenorreas (very irregular rules).
Following these ovulatory abnormalities, increased difficulty is evidence for pregnancy.
It can also be associated other pathologies characteristics of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, such as insulin resistance, obesity, diabetes, hypertension or hypercholesterolemia.
Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
 Among the most common symptoms of PCOS include:
Among the most common symptoms of PCOS include:
- Irregular cycles or amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
- Acne, even into adulthood.
- Hirsutism: excessive hair growth in areas of the face, abdomen, chest or around the nipples.
- Overweight / obesity
- Difficulty getting pregnant.
- Acanthosis nigricans, which is the appearance of dark marks on the skin folds (armpits, English, under the breasts ...).
- Lower density of the scalp and male pattern baldness (hair loss especially in the front area).
Diagnosis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
The diagnosis of PCOS has 3 components:
- Clinical component, associated with the symptoms described.
- The ultrasound component, which enlarged ovaries volume are observed on its periphery microcysts. There is 20% of the population can present this sonographic pattern without having PCOS.
- The hormonal component, which is checked with a blood test.
SOP associated with the risk of developing metabolic syndrome, consisting of obesity, changes in cholesterol, insulin resistance, high blood pressure increases. This can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
The purpose of treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is based on two pillars: the regularization of the menstrual cycle and the restoration of ovulatory cycles.
The first thing to do is consult with our doctor or gynecologist who made us several pretreatment tests: a study of ovarian function, a scan to detect the possible presence of cysts in the ovaries, different tests for hormone levels, insulin resistance tests and thyroid function.
Depending on the test results will decide the treatment to be carried out. In some cases normalization of the menstrual cycle can be performed only using oral contraceptives, but often require the combined with other methods.
If our doctor has detected that have a high resistance to insulin, for example, you can opt for a treatment with metformin associated with diet and moderate exercise. Thus it is achieved decrease insulin resistance and the likelihood of type 2 diabetes.
Clomiphene citrate is one of the most used treatments to restore ovulatory cycles. It works by blocking the estrogen receptors, and this leads to produce more stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which normalize ovulation. In cases where no ovulatory cycles are achieved despite clomiphene citrate may be administered gonadotropins, hormones that facilitate the proper maturation of the ovum.
As a last resort the doctor can use laparoscopic surgery for a "ovarian drilling". It is to perform different perforations in the ovarian cortex in order that the number of cysts is reduced, and hormonal levels and normalize the menstrual cycle.
In treatment of PCOS multiple alternatives exist, which depend on the patient's symptoms and whether or not pregnancy. Among them are life habit changes (decreased weight can be enough to regulate ovulation and improve symptoms), medical treatment (especially the use of oral contraceptives), et c.



