Relationship between diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease
Written by:A risk factor to suffer gingivitis and periodontitis is diabetes mellitus. Several studies conclude that glycemic control in diabetes disease is a variable in the initiation and progression of periodontal disease. The patient SRIS influences the prevalence and severity of periodontitis, rather than pathogenic bacteria.
Diabetic patients have altered function of some immune cells, which increases the production of inflammatory mediators. These meters are also present in the gums, which can increase inflammation and attachment loss and bone. Also, changes also occur in the synthesis and maturation of collagen, which degrades and affects periodontal healing, contributing to their destruction.
Symptoms of periodontitis in patients with diabetes mellitus
Patients diagnosed with diabetes mellitus have therefore increased risk for periodontal disease. This has two major consequences: the possibility of tooth loss and worse diabetes control.
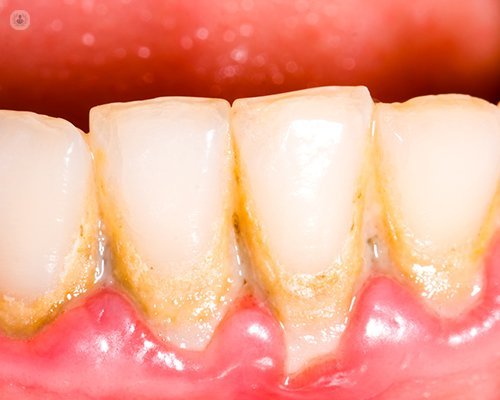
Symptoms that warn of the possibility of having periodontitis if you are diabetic are:
- Redness, bleeding and / or inflamed gums
- Suppuration
- Bad taste
- Longer teeth, apparently
- Mobility or tooth spaces
- Accumulation of tartar or calculus
- dry mouth
- Burning sensation
- Fungal infection
- Worst wound healing
Association between periodontal disease and diabetes
Furthermore, chronic inflammation due to periodontal disease has, in turn, impact:
- The glycemic control
- Complications of diabetes (cardiovascular, cerebrovascular or peripheral vascular)
- The role of beta cells of the pancreas
- The insulin resistance
- The future development of type 2 diabetes
Also, although the association for both diseases is emerging for type 1 diabetes and low for gestational diabetes, yes there is evidence of an association between periodontitis and type 2 diabetes. This means that patients with advanced periodontitis suffer an increase in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) in patients with type 2 diabetes and even in those without diabetes. In addition, periodontitis may start or increase insulin resistance in the same way as obesity, which is worse blood glucose control.
Treatment of periodontitis in patients with diabetes mellitus
Regular dental checkups by the expert recommended Dentistry as part of diabetes management, as well as making a careful dental and gums at home hygiene, for good maintenance of oral and systemic health.
It has been shown that after 3 months of treatment scaling and root planing, an average reduction of HbA1C is given of 0.36%. These reduction levels glycosylated hemoglobin short term equivalent to add a second drug to treat diabetes, making the mechanical treatment in a treatment of choice. Type 2 diabetic patients follow, in these cases, mechanical treatment and good oral hygiene monitoring. Patients with poor glycemic control could present, however, increased disease recurrence and response to treatment less favorable long term.



