The keys otitis
Written by:The ear is ear inflammation or their tissues. This is a very common pathology in children:an estimated 19% of children between 4 and 24 months have suffered ever
.
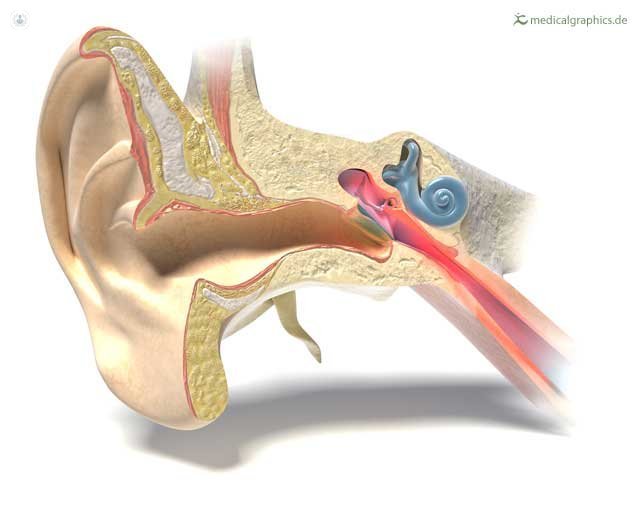
Causes
otitis are due to the inflammation of the Eustachian tube, which will not allow the middle ear ventilation and has the same atmospheric pressure that exists in abroad.
Then, the middle ear mucosa produces a secretion that occupies this area and can get infected, causing pain, fever and, ultimately, the tympanic membrane rupture outwards and the and liquid oozing out.
The eustachian tube ignites when neighboring structures adenoids and tonsils are in turn infected or inflamed, but can also give allergy or malfunction for its more horizontally situation in babies or malformations.
Otitis in children
The otitis most common infectious disease of childhood. For many pediatricians, is the most frequent cause of visit and diagnosis of disease. It has also been considered as the most frequent cause of illness after the common cold.
19 % of children between 4 and 24 months have a otitis. Children can be divided into three groups of approximately equal size in relation to otitis:a group without disease, another group with occasional otitis and a third with a susceptibility to otitis
.
There otitis relations with some personal traits: some breeds are more predisposed, as American Indians, Australian aborigines or gypsy children. There is also a relationship with poor social and economic status or living in overcrowded, although the causes are unknown.
Moreover, it has been established that children breast-feeding for 12 months have less otitis that artificially or breast-fed for one month.
Treatment
To treat otitis Antibiotics are administered broad-spectrum cephalosporin or resistant cases, in addition to antiinflammatory and exceptionally oral corticosteroids.
To maintain an open nostrils, we use sera or solutions sterile sea water, which help clear secretions from the nose. In more persistent cases, you can use topical nasal corticosteroids who act locally.
Surgery
It is considered resorting to surgery when the repetition of the causes otitis hearing loss more than 3 months duration or occur deformities of the tympanic membrane.
In these cases, it is usual to put drainpipes in the tympanic membrane, called ventilation tubes. These allow ventilation of the middle ear and make more difficult the appearance of mucus and infection. In short, replace the function of the eustachian tube until it recovers from its pathology.
When there hypertrophic adenoids ( vegetations ) that block the eustachian tube or facilitate the inflammation, we proceed to remove them, a process called adenoidectomy.
The same applies to the palatine tonsils ( anginas ), which is also extirpated in the event of repeated inflammatory injuring the eustachian tube ( tonsillectomy ).
Possible complications of otitis
Complications are exceptional in this disease. As otitis develops in the middle ear, complications reach those upcoming areas such as the inner ear.
This can occur, for example, a labyrinthitis ( swelling of the inner ear ) that causes dizziness and loss of hearing or affectation of facial nerve paralysis.
Still, the most frequent complication is the mastoiditis, which is the inflammation of the area behind the pinna with pain and redness.
Prevention
The best way to prevent otitis is vaccinated against germs (mainly pneumococcus ) that cause infection of the middle ear.
Another method of prevention is the chemoprophylaxis, ie, administer antibiotics to patients for long periods of time even without the disease.


