Ptosis, causes and treatments
Written by:What is it?
The medical term ptosis defines a situation in which a fall of the upper eyelid occurs. This decrease may cause, apart from the aesthetic problem, a decrease in visual acuity due to occlusion of the pupillary axis by the eyelid or a decrease in the superior visual field. Patients often try to open their eyes by raising their eyebrows to compensate for the loss of function of the eyelid lift muscle with the frontalis muscle.. Due to this effort, many patients complain of fatigue in the frontal region and heaviness in the eyelids.
Sometimes, they resort to the fingers to elevate the eyelids. In children, apart from the aesthetic problem, the occlusion of the visual axis by the eyelid can give rise to the vague eye .
What causes it?
There are multiple causes of ptosis. The most frequent, in adults, is due to a disinsertion of the levator palpebrae muscle that is the maximum responsible for the function of the eyelid rise. Other causes of disinsertion are eye surgeries or prolonged use of contact lenses. In children, the most common cause is a congenital weakening of the levator muscle. However, there are other less frequent causes such as muscular diseases (dystrophies, myopathies, myasthenia gravis ...), neurological diseases or traumatisms.
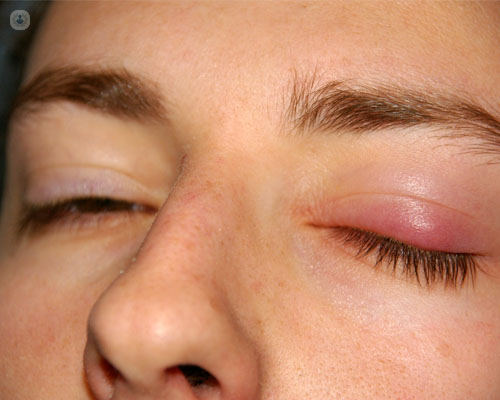
How are they treated? What results are obtained?
Except in exceptional cases, associated with neurological diseases, most ptosis have surgical treatment. Normally, the intervention consists of shortening or reinsertion of the levator muscle through an incision in the palpebral groove, so that the scar is disguised. In cases of extreme weakness of the levator muscle, surgeries called frontal suspension can be performed, consisting of the placement of bands of autologous material (of the patient) or inert synthetic material, through small incisions in the eyelid and forehead. , which allow raising the eyelid taking advantage of the function of the frontal muscle. There are other interventions, less common, that are based on shortening of small muscles of the eyelid called conjunctivomullectomy.
In all cases, before proceeding to the surgical correction of the ptosis, a study and a correct exploration must be done that will determine the type of intervention to be performed in each specific case.. The objective of the surgery is to improve the aesthetic appearance , seeking the greatest possible symmetry between the two eyes, and a correct palpebral opening and closing.
Normally, the results are satisfactory, although there is a percentage of reinterventions that oscillate between 5-20% of the cases, depending on the different surgical techniques and the complexity of the pictures. Like any other surgery, ptosis surgery is not free of risks and complications such as the impossibility of palpebral closure (lagophthalmos), hypocorrection, hematoma and eyelid edema, alterations of the eyelid margin shape, infections and granulomas.. The oculoplastic ophthalmologists have been trained, for years, in the different surgical techniques for the correction of ptosis and are the best trained to solve the potential complications that may arise in the postoperative period.


