Cerebral hemorrhage: what are the symptoms and how is
Written by:Cerebral hemorrhage is the appearance of a quantity of blood within the brain parenchyma and that will give rise in most cases, a neurological deficit of some consideration.
Risk factors for cerebral hemorrhage
The most important risk factors of general hemorrhage include age, gender (more men), race (more in blacks than in whites), alcohol and drugs, and liver dysfunction.
Causes of Cerebral hemorrhage
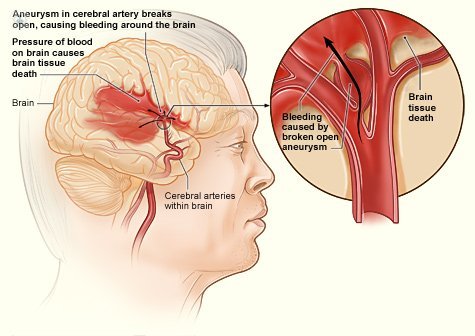 The main causes of cerebral hemorrhage are:
The main causes of cerebral hemorrhage are:
- Either acute or chronic hypertension
- Processes that increase cerebral blood flow
- Vascular abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations or aneurysms
- Arteriopathy, amyloid angiopathy being the most common
- brain tumors
- coagulopathy
- brain infections
Symptoms of cerebral hemorrhage
Cerebral hemorrhage usually has a mild start progressing in minutes or hours. This difference of stroke (ischemic or embolic), whose onset is abrupt.
The symptoms are headache, vomiting and altered level of consciousness. If this last symptom progresses can lead to coma and ultimately death of the patient.
Most clinical signs are found hemiplegia, hemianopia hemisensory or varying degrees of involvement can reach up to the irreversibility of the damage.
Diagnosis of cerebral hemorrhage
The best and most rapid diagnostic test for the specialists detect a brain hemorrhage is computed tomography. The TAC not only shows the presence of blood in the brain parenchyma, but also the precise location of the same and detects if it is causing mass effect or expansion within the brain, which means further injury even than the initial bleeding.
Magnetic resonance imaging is another tool to use in case there is suspicion of the existence of an underlying condition, such as a vascular malformation or a tumor.
Treatment of cerebral hemorrhage
In most cases the treatment will be conservative, trying to control blood pressure. If I were high, it should be reduced to the levels they had before the onset of clinical symptoms, more or less, but never below them, because that could lead to cerebral ischemic problems, which considerably aggravate the process.
Other measures to be applied are: correct problems with blood clotting and maintain a clear airway for good brain oxygenation.
Surgical treatment is very controversial in the supratentorial hemorrhages and have been several randomized multicenter studies have failed to show a benefit of surgery over conservative treatment.
However, when bleeding is intracerebelosa the surgical option must have it in mind.


