Social phobia, fear of people
Written by:Social phobia, also called social anxiety, is a mental disorder characterized by an intense fear of one or more types of social situations in which the person being observed or believe you notes.
Social phobia causes a number of changes in attitude and status of persons.
- Changes in your thinking: magnification of the criticism suffered by others. One of the main features of social phobia is the high early concern about a situation that is expected to be faced in the future.
- Changes in physiological responses: excessive sweating, muscle tension, rapid heart rate, shallow breathing and shortness.
- Changes in behavioral responses: repetitive movements, body language or excuses tension out of the situation.
- Affective changes: People with social phobia tend to avoid situations with excuses like "I do not fancy" or "prefer to be only" for not having to go through a negative public opinion.
People with social phobia try to avoid, insofar as possible, these situations. Or, they go through them trying at all costs others only perceive their anxiety response. This attitude of "not notice that ..." is one of the factors that influence that social phobia persists, as it prevents people affected by this disorder generates tools of emotional, cognitive and behavioral management.
Approximately around 10-13% of people experience social phobia at some point in their lives. Fear of public speaking is a very common type of social phobia.
What are the causes of social phobia?
The origin of the disorder, or social phobia is different possible causes. On the one hand, there is some predisposing biological vulnerability to social phobia, ie a hereditary component. Some people tend to be socially inhibited and intensely experience anxiety.
The educational factor is also a possible cause of social phobia. The social models influence to tackling or avoid certain situations. As also they influence their own social experiences. For example, there are people who feel public criticism as an experience especially harmful. Given these experiences, the person learns a set of beliefs that cause you to be unable to meet certain social situations and unable to successfully overcome with calmness and fortitude to negative criticism of others.
When these factors also added stressful life events, such as a family problem or job stress, the likelihood of developing social phobia increases.
Treatment for social phobia
Treatment of Psychology of social phobia consists of two clinical tools: cognitive restructuring and exposure. Both tools have to work in parallel.
Cognitive restructuring aims to understand why the person perceives and interprets social situations serves as an insurmountable threat. Is a treatment by which cognitive mechanisms before the patient stops firmly believe that failure in front of others is likely catastrophic develop.
Furthermore, the exhibition seeks to relearn basic process: stop running in a situation of anxiety. The patient gradually overcome situations where anxiety longer the protagonist gradually.
The duration of psychological treatments for social phobia about 15 sessions.
If a person with social phobia do not receive psychological treatment, often serious consequences emotional and social level. Often some people with social phobia resort to alcohol or other substances in order to cushion the answers to the anxiety caused.
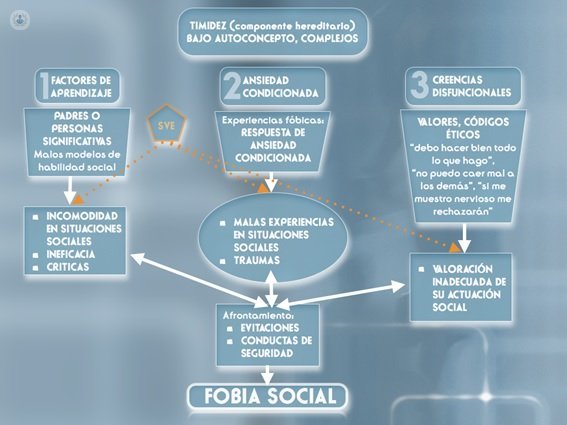
Source: merging several models or patterns of social foabia of different authors. By Julia Vidal



