When chicken pox appears?
Written by:Chickenpox is an infectious disease that appears after the initial contact with the virus. It may appear at any time of life, but in 90% of cases occur before age 10. The risk of infection marks having passed the disease or been vaccinated since last once (or vaccinated) immunity for the rest of life is maintained.
The contagiousness of chickenpox is very high, it is considered one of the most easily transmissible infectious diseases, with rates above 90%. Diagnosis is clinical, it is done with the display of the typical lesions. Treatment is antipyretics and sometimes associated antihistamines.
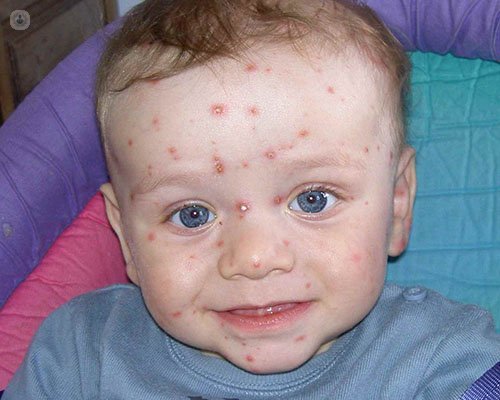
Varicella
Vaccination should be done in the early years of life, just when risk has to be suffered, since it is a disease not without complications and even death.
Currently, the recommendation of scientific societies is 12-15 months the first dose of vaccine, a second dose spaced at least 4 weeks.
If we look at public funding, in our country the first dose is administered since the 2016 at 15 months and the second dose at 4 years. This pattern, although considerably reduce the number of cases does not prevent some chicken pox vaccine gap or failure by a single dose, because it is not administered until more than two years and a half after the second dose. The optimum is administered from 12 months the two doses, spacing them including at least 4 weeks, thereby is achieved fully immunize the child and avoid unnecessary risks.
How to act in case of chickenpox
In case of chickenpox, the first thing is to isolate the affected, the child does not attend daycare or school and keep observed at home.
When making with vesicular lesions that are very itchy (itch a lot), the temptation to scratch is huge, therefore, to avoid permanent sequelae secondary to scratching, administer antihistamines. If present with malaise or fever, you may be given antipyretics, always avoiding aspirin risk of liver failure. Avoid topical painkillers Talquistina type, as they may encourage superinfection of lesions.
Sometimes antiseptics copper sulphate or zinc that help dry the lesions sulfate are used, but its use must be prescribed and administered as recommended by the pediatrician .
In addition, the contact should be avoided by pregnant be a population at risk of severe varicella for mother and especially to the fetus.


