How can you treat a brain tumor?
Written by:There are two types of brain tumors:
- primary; those originating in the neuroepithelial tissue in the meninges, cranial nerve, in blood cells, germ cells, in the region of the pituitary and those extending from adjacent regions.
- side; metastasis, ie, brain tumors implanted in the brain, but whose origin is a focus of the body other than the brain. For example, lung cancer can send cancer cells into the bloodstream and end up depositing in the brain and leading to the creation of a brain metastatic tumor. These tumors are the most common of all and, sometimes, if achieved properly treat the patient can be cured, provided the primary tumor is eradicated.
Risk factors for brain tumor
The main factor that greatly increases the risk of developing a brain tumor is exposure to ionizing radiation.
On the other hand, there are factors that have been attributed some influence (although so far no scientific confirmation): some environmental factors, such as food, snuff, use of mobile phones, etc.
Symptoms of brain tumor
The most common presentation of a brain tumor is a progressive neurological deficit; usually a loss of strength in a limb. The headache is also a frequent symptom onset and seizures.
Other symptoms may include mental disorders such as depression, apathy, drowsiness or confusion. Also nausea and vomiting can manifest, more usually in tumors in the region of the cerebellum and brain stem, or visual and endocrine disorders in pituitary tumors and its region.
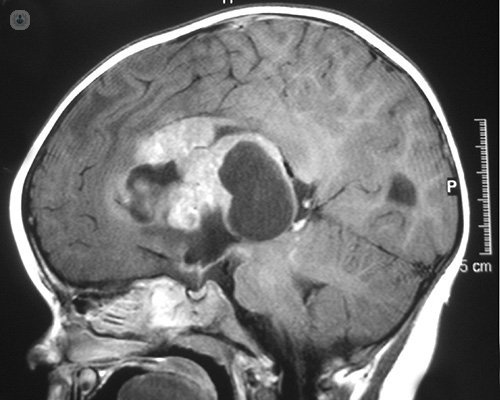
Brain tumor diagnosis
Start diagnosis of a brain tumor is usually computed tomography (CT), commonly called scanner. This is because it is the fastest and easiest method to make a first approximation.
When a patient has any of the symptoms mentioned previously consult the specialist in neurosurgery , but most of the time it will going to an emergency room, given the alarm is generated.
Subsequently, the second diagnostic test to be performed will be a brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which will give us many more details of the tumor, especially in terms of their nature, location, behavior and involvement of eloquent brain areas, such as the motor, sensory or visual areas, or language or region of the brainstem as well as the gray nuclei of the base, etc.
Other diagnostic tests, and in a second line of importance, cerebral angiography, if we suspect that the tumor will have much blood supply, or neurophysiological tests (electroencephalogram, evoked potentials).
Treatments for brain tumor
In recent decades it has been achieved an enormous amount in the diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors. The CT and MRI have made it possible to make a fairly early diagnosis of a brain tumor, allowing time to catch a lot of these injuries. We also do have a very rough idea of the precise location of the tumor and its relationship to adjacent structures, many of which have important functions and therefore should be treated with great care.
Another essential step is to have the help of neuronavegador. Thanks to him we can locate almost complete accuracy a brain tumor and not cause damage to surrounding structures during performing surgery. These devices also give us the option to take a millimeter biopsy of a brain tumor with extreme rigor, which can give us the histological diagnosis of the process without having to approach it with large operations and, most importantly, without damaging the tissue brain tumor located around. This approach is usually done in tumors are malignant and suspect that are located deep in the brain, where access is very limited. And the result histologic confirmation of malignancy and would act accordingly, possibly with radiotherapy and chemotherapy alone.
Other tools that work in the operating room are usually intraoperative MRI and CT OARM that help us make decisions during surgery and perform the surgery itself.
In the surgical treatment it is necessary to highlight the ultrasonic aspirator which facilitates removal of tumors by fragmentation (ultrasound) and aspiration of tumor tissue without causing significant traction which could be harmful.
Meanwhile, neuroendoscopy has meant another step in the surgical treatment of some brain tumors located at the base of the skull and in the midline. Thanks to her, the approaches are less invasive and excellent results.
Radiosurgery is a treatment modality that consists of giving radiation therapy in a targeted and very precise on a generally deep brain tumor, avoiding radiation on surrounding brain tissue. This therapeutic modality, but it does not eliminate the tumor, get -in most cases slow its growth.


