How to tell if you suffer and how to treat epicondylitis
Written by:Epicondylitis (tennis elbow or) is an injury that causes pain on the outside of the elbow. The cause lies in repetitive wrist extension and forearm supination. This causes fibrillar micro - breakages and improper repair of the tendons of the muscles that originate in the region, mainly short radial extensor tendon carpi.
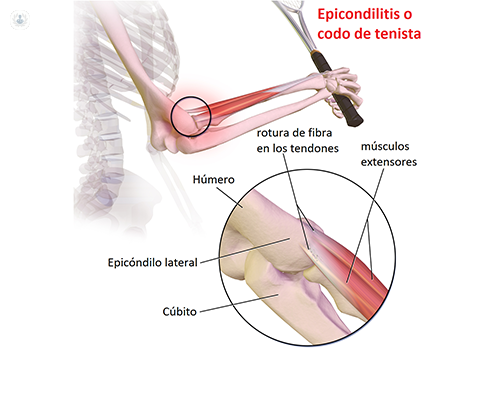
It is the inflammation of the tendons epicondylar, which are giving rise mainly to the extensor muscles that originates from the epicondyle, on the outer side of the elbow and reaches his hand.
When these muscles and again used, small microlesions produced tendon. Over time this leads to irritation and pain in the outer elbow. In general, any activity that involves repetitive twisting of the wrist can lead to this injury.
It is caused, then, by these repetitive movements of extension and supination of the forearm, causing tendinitis in the muscles and tendons in that area. The final epicondylitis is caused by repeated microtrauma.
Inflammatory changes occur in acute processes, but these do not occur if the injury is chronic epicondylitis ago. In this phase it is passed to speak of tendinosis and is a degenerative process of the tendon fibers.
Prevalence of epicondylitis and groups with increased risk of suffering
The incidence of epicondylitis occurs mainly between 34 and 54 years. Although no involvement have shown differences between men and women, yes it is known that the injury is more common in corresponding to the dominant hand side.Also, some professionals of certain sporting activities (especially those racquet) and professions are more likely to suffer from epicondylitis, the fact repeat a particular gesture. Some examples are: painters, mechanics, factory workers or people who work long hours at the computer, managing the mouse.
Symptoms or warning signs to suspect epicondylitis
There are certain symptoms that can warn of a possible epicondylitis:- Pain on the outside of the elbow.- Pain and functional while performing wrist extension and forearm supination impotence.- Painful feel the epicondylar area.- Pain when running simple actions like lifting a bottle or a cup of coffee. Also when executing a backhand in tennis or paddle tennis, for example.- If these symptoms do not subside with rest relative, local cold and treatment with anti-inflammatory or aggravated by everyday actions.
How to prevent epicondylitis
Postural hygiene is the best method to prevent epicondylitis. Make proper moves to make sport or at work will cause the tendons are not subjected to excessive stress.Furthermore, resting his elbow after sessions of strong activity helps prevent injury. They will be very beneficial in this regard, stretching and preventive massages and use orthotics or elbow pads.
Treatment of epicondylitis
The treatment applied experts Traumatology should follow a logical order, moving from more to less, as if a ladder is ascended:
1) In the first step they would be found:a. Nonsteroidal anti - inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) administered orally or topically with creams or gelsb. Rest of the joint. Reducing activities that cause pain, decreasing the time and intensity of activity.c. Physical therapy, with the local application of heat, ultrasound, electrotherapy, laser, massage techniques, shockwaves or certain exercises and techniques.
2) In the second step would be:
a. Infiltration. They are local injections of corticosteroids, associated or not with an anesthetic. Which they are injected around the epicondyle can solve the pain for weeks or months. Sometimes 3 successive infiltrations are applied at intervals of 1 or 2 weeks apart. As there is little risk of local failure of tendon insertion and tendon, infiltrations limited to 3. In this regard, recently, it uses infiltration platelet rich plasma, although not shown to have greater efficacy than corticosteroids.b. Occupational therapy. movements that cause epicondylitis is recommended to limit. An ergonomic study of workplace avoid repetitive movements that cause, which would be key to the cure rate.
3) In the third step of the surgery would be used:a. Operation epicondylitis. It is recommended in certain cases that do not respond to the above measures. It can intervene with an open incision or arthroscopically. The advantages reside in arthroscopy allowing treat injury through two small incisions, inserting a camera into the joint. In addition to being less invasive and allow faster and less painful recovery, allows explore other possible intraarticular injuries that cause pain in the outer elbow and may be confused with epicondylitis (synovial plates, articular cartilage lesions or inflammatory processes). In addition, intervention is usually performed on an outpatient basis and under locoregional anesthesia in the arm.
Edited by Patricia Crespo Pujante


