Hip replacement surgery: causes, functioning and tips
Written by:Patients undergoing implantation of hip prosthesis suffer osteoarthritis, a degenerative chronic disease that affects joint cartilage. This does not mean that all patients with osteoarthritis have to be operated hip as some can improve their quality of life with medical treatment, and stretching exercises.
For this reason, the orthopedic surgeon should recommend hip replacement surgery only patients who have many limitations in the hip joint function involving them progressive pain and impede the basic tasks of your daily routine.
Patient Profile: osteoarthritis
The profile of the patient who undergoes hip surgery usually takes between 65 and 75 years when hip osteoarthritis is more advanced. In younger people, there are cases of some diseases early osteoarthritis or joint degenerating due to trauma, abnormal blood flow in the femoral head, among others.
The patient usually feels pain in the groin when he joined the chair, when walking, when up and down stairs, when you put a sock when gets on the bus when crossing legs, among other situations.
Also keep in mind that you should never assess only hip radiographs to determine whether osteoarthritis is moderate or severe, but have to study radiography in conjunction with clinical examination and the patient's symptoms.
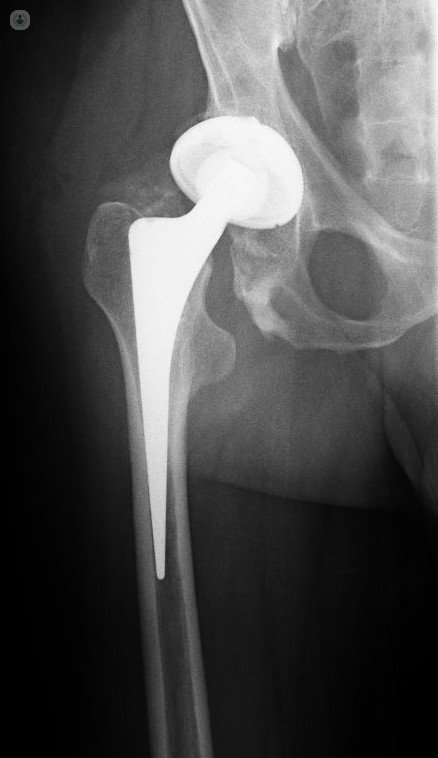
How the hip prosthesis is placed
The hip prosthesis is a "metal hip" replacing the hip joint by surgical intervention. To place the prosthesis, open surgery is needed, with a scar about 10 cm to have a good view of the hip.
Total hip replacement is characterized by having a femoral component and a pelvic or acetabular, both linked by a metal head and a plastic component (polyethylene very high density), which operate as joint.
Recovery from hip surgery
This procedure usually requires a hospital stay of five to seven days, although the patient begins to lean and walk from the second or third day with the help of a walker or canes. During these early days, it is important to control the pain with medication, for example, through an epidural catheter inserted in the back.
In the first weeks of recovery, the patient must follow a set of basic recommendations to avoid possible complications in the future:
- Go to physiotherapist: it will help to stop the walker and canes gradually and restore function of the hip • Do not cross your legs
- Avoid forced rotation of the hip replaced • Do not sit on low seats
- Place an item in the toilet
- showering sitting
- Walking often, but always with an extra support to feel safe
The hip replacement surgery usually achieved eliminate pain and the patient recovers functionality in most cases.


