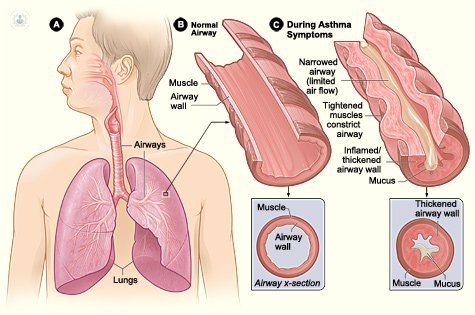
Chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis, also known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), is the persistent inflammation of the lining of the bronchi causing dyspnea, mild persistent cough and mucus. According to its progression, shortness of breath may limit the ability of the person to lead a normal daily activity. Among its most serious complications include pulmonary hypertension, gasping and/or choking breath, chronic obstruction of the bronchi, and the development of pneumonia, tuberculosis and emphysema. Its origin is associated with several factors:persistent cough with phlegm, characteristic of a bad cold curing; tobacco, 80% of cases; Continuous exposure to fumes, dust, or agents that irritate the mucous own work activities; or relatively rare inherited deficiency of a protein called alpha-1-antitrypsin, which protects lung tissue inflammation caused by infections and certain irritating inhalation, as smoke snuff. The most effective treatment to reduce irritation of the bronchial tubes are the abandonment of smoking, as well as the administration of antibiotics, expectorant drugs (except antitussives), and the use of bronchodilators (to open the airways). When chronic bronchitis is severe is needed sputum culture to check the need for a change in treatment.