Brain aneurysm
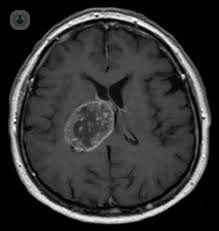
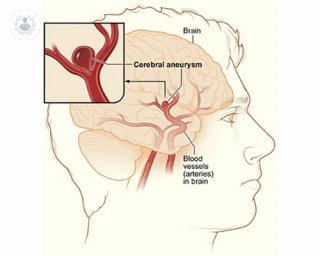
Aneurysms are dilatations of the arteries due to a fault in the vessel wall which triggers an increase in diameter and carries the risk of rupture and massive internal bleeding. A cerebral aneurysm, also known as intracranial aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel in the brain. It can be congenital, but they can also be traumatic cause, tumor, for arteriosclerosis, by common infectious cause or drug consumption. Depending on the shape of the aneurysm are divided into secular, fusiform, and use as side; They may also be classified by size. All aneurysms may be complicated by rupture of the vessel and cause bleeding in the brain, causing a stroke acidente, which can cause irreversible nerve damage. Aneurysms are asymptomatic, symptoms only when they break, causing intense headaches, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, seizures or sudden loss of consciousness. For diagnosis, several tests such as angiography or CT are used, and the treatment depends on the size of the aneurysm and associated risk factors. There are several alternatives for both conservative and surgical treatment, which must evaluate a neurosurgeon.