FAQ for spasticity
Written by:What is spasticity?
Spasticity is a symptom present in different neurological diseases. It is an increase in the tone of one or several muscles , which prevents them from relaxing. This fact causes forced postures: in the upper limb it can cause the shoulder to be stuck to the body, the elbow and the wrist to flex or the hands to close; in the lower limb, causes hip and knee flexion, the appearance of equinus (with the tip dropped) or the raised big toe. Occasionally contractions or involuntary spasms also appear.
What are your causes?
Spasticity can have its origin in any disease of the central nervous system , cerebral or spinal. In this there is an alteration of the stretch reflex of the muscles, which therefore does not relax as they would normally after their contraction. Some of the diseases that produce spasticity are stroke (hemiplegia), spinal cord injury (both paraplegia and tetraplegia ), multiple sclerosis , traumatic brain injury , or infant cerebral palsy , among others.
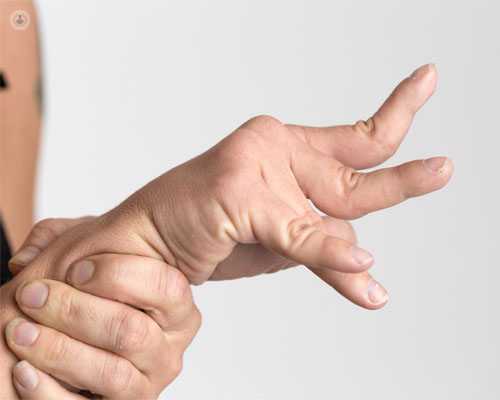
What symptoms does it present?
The symptoms of spasticity are diverse, since they depend on the intensity of the disorder and the muscles affected (it is not the same if there is spasticity only in one limb that is present in a large part of the musculature).
In general, the most common symptoms are pain and limited functionality and independence of the person suffering from the disorder.
When it is present in the upper limb it causes shoulder pain and also the patient has difficulties in the hygiene of his armpits, because he can not separate the arm enough. For the same reason you can not clean your hands or cut your nails properly. This lack of involuntary hygiene can lead to infection in the hands or in the armpit. She will also have difficulty getting dressed and undressing because she can not move her shoulder or elbow joints.
As for the lower limb, the ability to walk is affected (for example, the tip of the foot dropped in cases of equine foot causes habitual falls since the patient can easily trip). When the adductor muscles are affected, there are difficulties in this sense, as the legs interlock involuntarily. This also makes genital and perianal hygiene difficult and also hinders sexual relations.
The spastic patients also have many difficulties when correctly placing the orthoses of both the upper limb and the lower limb. This causes the abnormal positions of the joints to remain.
How should it be treated? Do you have a cure?
Spasticity does not have a definitive cure, since it is a symptom and not a disease. Being produced by an irreversible neurological lesion , the damages produced by it remain in time.
However, it has effective treatment. The type of therapy used is different depending on the number of muscles affected.
When spasticity is focal (that is, it affects only a few muscles of the body), the most appropriate treatment is infiltration with botulinum toxin.. This substance is injected directly into the muscle and produces its relaxation. Its effectiveness translates into an improvement in the quality of life both of the patient himself and of the people in charge of his care, since joints can be moved passively and easily in which mobility was previously practically impossible.
The relaxation of the musculature with the injection of botulinum toxin allows to diminish the pain caused by the contraction maintained of the affected musculature and, secondarily, it improves the quality of the sleep and the form of sitting or lying down. It also usually improves the ease of dress and undress, hygiene, etc.
The effect of botulinum toxin is temporary over time: it lasts around three or four months, so to maintain the therapeutic effects it is necessary to perform periodic infiltrations.
It is a safe drug when used by specialists (rehabilitators or neurologists) experts in Neurorehabilitation. The experience in the use of botulinum toxin both in Spain and in the rest of the world is more than 25 years. During this time, its effectiveness and the lack of unwanted effects have been documented.
When spasticity is generalized, that is, it affects the vast majority of muscles of the body, the isolated use of botulinum toxin is usually not enough, as it would no longer be safe.
In these cases the treatment of choice is therapy with intrathecal baclofen , if oral therapy has failed (which is often the case). It consists in the surgical implantation of a system that directly administers the medication (baclofen) in the central nervous system. This decreases the generalized spasticity and great benefits are achieved for the quality of life of the patient and their caregivers.
Sometimes both therapies (botulinum toxin and intrathecal baclofen pump) are combined to achieve better results.


