Prevention of peri-implant disease from surgical planning
Written by:Before implant placement, prior planning is necessary, which consists of an evaluation and thorough analysis to avoid future occurrence of such common peri - implant diseases.
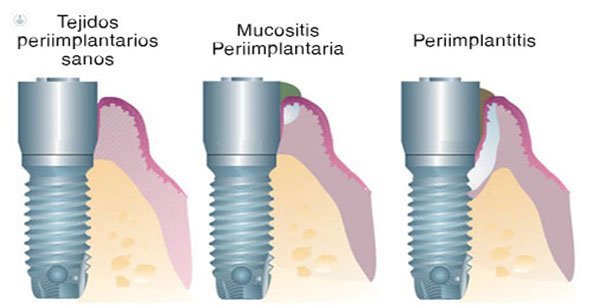
periimplant mucositis and periimplantitis, both described as infectious entities: these diseases according to two clinical entities described.
- Periimplant mucositis is characterized by the presence of inflammation in the peri - implant mucosa without signs of bone loss. Usually reversible.
- Periimplantitis: is also accompanied by bone loss marginally support once completed the normal bone remodeling process. The reversal in the periimplantitis is more complicated than in mucositis.
Prevalence of peri - implant diseases
The estimated prevalence for these two entities varies greatly depending on the design of the study and definition of the disease. In 2008 it was established that the peri-implant mucositis occurred in 80% of patients and 50% of implants, while perimplantitis was identified between 28 and 56% of patients and between 12 and 43% of implants.
In a recent systematic review (2015), a prevalence of mucositis and periimplantitis 43% and 22% respectively stated.
Risk factors for peri - implant diseases
European Workshop on Periodontology 2008, numerous risk indicators identified classified as major or minor evidence. So they were considered strong evidence of poor oral hygiene, previous history of periodontitis, and smoking; medium evidence, diabetes and alcohol consumption; finally, low evidence of genetic susceptibility and the surface of the implant.
Moreover, evidence is growing as a risk factor the residual cement after placement of a restoration. An additional factor that has been named is the occlusal overload.

Treatment of peri - implant diseases
The treatment protocol is complex and without consensus. Today there is no standard treatment, different therapeutic options, but there are some more scientific evidence.
Treatments for peri - implant diseases are proposed evidence - based treatments for periodontal diseases.
Debridement (removal of biofilm) on the implant surface is the basic element in the treatment of mucositis and periimplantitis. nonsurgical and surgical Two types of treatment are distinguished. With regard to the peri-implant mucositis was approved nonsurgical treatment caused reduction in inflammation (BoP) in combination with the adjuvant use of antimicrobial rinses. However, non-surgical treatment for perimplantitis was unpredictable.
The main objective of surgical treatment of periimplantitis is access to the implant surface to desbridarla and decontaminated and thus achieve the resolution of the inflammatory lesion.
Normally, surgical techniques and reconstructive procedures are more effective but limited to moderate and severe periimplantitis.
Among the surgical treatment of periimplantitis more scientific envidencia are presented:
Resective surgery: decontaminated implant surface and exposing the affected area to implant the oral cavity by sweeping a flap repositioning it in a higher position for a better hygiene self. It is often accompanied by a osteoplastia (smoothing the surface of the implant left exposed, remove the coils in that area). This technique is very similar to periodontal surgery done in natural dentition, which reduces the depth of bags, facilitating patient hygiene. This technique has clear disadvantages and is only recommended for regions without aesthetic compromise.
 Access surgery: a surgical way to decontaminate the surface of the implant, keeping the soft tissue around the implant affected. It is recommended when bone loss is minimal. Access surgery can be combined with various methods such as scalers, air abrasion devices, ultrasonic devices and lasers to improve their effectiveness.
Access surgery: a surgical way to decontaminate the surface of the implant, keeping the soft tissue around the implant affected. It is recommended when bone loss is minimal. Access surgery can be combined with various methods such as scalers, air abrasion devices, ultrasonic devices and lasers to improve their effectiveness.
 Regenerative Surgery is mainly used to support tissues and avoid recessions in the mucosa. After decontamination of the implant surface should be placed around the implant graft, filling the peri-implant defect. The most commonly used implants are both self patient's bone as bone substitutes. Furthermore, the use of connective tissue graft in combination with a bone graft can have great aesthetic advantages. The long term goal of a regenerative process is re-adhesion periimplant soft tissue and improved bone regeneration around the implant surface.
Regenerative Surgery is mainly used to support tissues and avoid recessions in the mucosa. After decontamination of the implant surface should be placed around the implant graft, filling the peri-implant defect. The most commonly used implants are both self patient's bone as bone substitutes. Furthermore, the use of connective tissue graft in combination with a bone graft can have great aesthetic advantages. The long term goal of a regenerative process is re-adhesion periimplant soft tissue and improved bone regeneration around the implant surface.
In short, to prevent the occurrence of future peri - implant disease, have identified a number of variables that specialists in dentistry must take into account when performing surgical planning, since they intervene in increased plaque around implants and consequently their bone loss.
It is essential that professionals identify these variables, from surgical planning to control them and even if necessary, modify the treatment protocol as an important step in reducing the prevalence and risk of peri-implant disease step.


